When purchasing a metal laser cutting machine, many customers are curious about what is kerf in laser cutting, especially the width of the laser cut, which has a great impact on the cutting quality. This blog post will explain laser cutting kerf, and I hope it will be helpful to you.
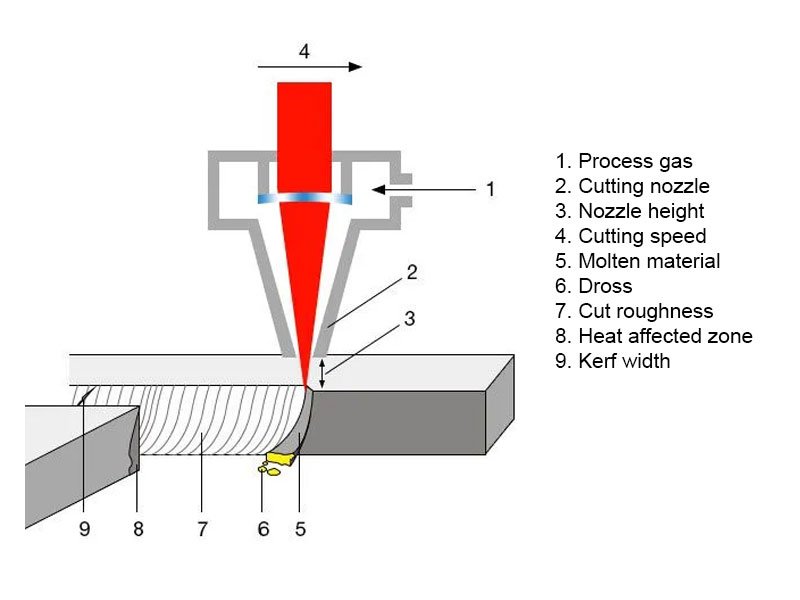
What is the kerf of a laser cutter
Laser cutting kerf refers to the cut formed when the laser beam irradiates the material during the laser cutting process. Laser cutting is a technology that uses a high power laser beam to cut materials without contact.
What is the kerf in a laser cutting system

Factors affecting the size of laser cutter kerf
- Thickness of the material being cut: Generally, the kerf should be slightly larger than 60-80% of the material thickness.
- Welding part size and design requirements: The size of the kerf should be set based on factors such as whether the weld is fused together or a slight gap is required.
- Cutting speed: The faster the speed, the wider the kerf; the slower the speed, the narrower the kerf.
How to design laser cutter kerf size
In order to produce high-quality and efficient parts, the appropriate incision size should be determined in combination with the characteristics of the workpiece itself.
- For thin plate materials, the incision should be greater than 60% and less than 80% of the material thickness.
- For materials with a thickness of more than 5mm, the incision size should be at least 45% of the material thickness.
- When bending parts, the incision size is usually less than 50% of the material thickness.
- For parts that need to be welded, the incision size is usually slightly larger than 50% of the material thickness of the welding part.
What is Compensating the kerf width
Compensating the kerf width is an important concept in the laser cutting process. It refers to the operation of compensating the kerf width produced by laser cutting during programming and actual cutting.
What are the software for setting the compensation slit width for laser cutting machines?
- CorelDRAW: This is a widely used vector graphics design software that provides laser cutting functions, including slit width compensation settings.
- AutoCAD: Although mainly used for CAD design, AutoCAD can also be used with laser cutting machines and provides slit compensation functions.
- LightBurn: This is a software designed specifically for laser cutting and engraving, with an intuitive slit compensation setting interface.
- RDWorks: This is the software that comes with many Chinese-made laser cutting machines and provides comprehensive cutting parameter control, including slit compensation.
- LaserCut: Another software commonly found in Chinese-made laser cutting machines, with slit compensation functions.
- CypCut: Software specifically for fiber laser cutting machines that provides precise slit width control.
- BySoft: Software developed by Bystronic for its laser cutting machines, with advanced slit compensation functions.
- Lantek Expert Cut: This is a professional sheet metal processing software that includes laser cutting and slit compensation functions.
These software usually allow users to enter material type, thickness and other relevant parameters, and then automatically calculate the appropriate slit compensation value. Some more advanced software can even automatically adjust and optimize based on the actual cutting results.

How to set the compensation slit width of laser cutting machine
Determine the actual kerf width:
First, you need to measure the actual kerf width. This can be done by cutting a test sample and then using a precision measuring tool such as a micrometer to measure the kerf width.
Adjust the design dimensions:
Based on the measured kerf width, adjust the design dimensions. Typically, for external contours, increase the kerf width by half, and for internal features, decrease the kerf width by half.
Consider material properties:
Different materials have different cutting properties that affect the kerf width. For example, the thermal conductivity and reflectivity of metals affect the kerf width, while the melting point and thickness of plastics are also important factors.
Adjust laser parameters:
Parameters such as laser power, cutting speed, and focus position all affect the kerf width. These parameters need to be optimized based on the material type and thickness.
Use software tools:
Many modern laser cutting machines are equipped with software that automatically calculates and applies kerf compensation. The operator can enter the material type, thickness, and other relevant parameters, and the software automatically calculates the appropriate compensation value.
Test and fine-tune:
Once the setup is complete, make a test cut and check the results. If necessary, make fine adjustments to achieve the best results.
Consider the cutting method:
Different cutting methods (such as fusion cutting, flame cutting, etc.) may require different compensation settings.
Regular calibration:
Since laser performance may change over time, regular calibration and adjustment of compensation values are necessary.
By accurately setting the compensation kerf width, you can ensure the dimensional accuracy of the cut parts, improve material utilization, and achieve high-quality cutting results. This is especially important for applications that require tight tolerances and high precision.

In laser cutting, male cut, female cut, ring cut, how to distinguish?
- Positive cutting: The lead position will be outside the pattern, which is suitable for finished products within the cutting line.
- Negative cutting: The lead is placed inside the cutting pattern, which is suitable for workpieces that require an outer circle, such as: a large square box with a small square box, and the small square inside the square box is not needed.
- Circular cutting: It is suitable for cutting thin plates, and there will be over-burning and corner burning.
How to reduce kerf in laser cutting
- Use high-power lasers: High-power lasers can provide more concentrated energy, allowing for faster cutting without increasing the kerf width.
- Optimize focus position: The focus should be set precisely on the cutting line of the material to ensure that the laser energy is concentrated in a smaller area, thereby reducing the kerf width.
- Choose the right cutting speed: The cutting speed needs to be optimized based on the thickness and type of the material. Too fast a speed may result in an uneven cut edge, while too slow a speed may increase the heat-affected zone, causing the cut to become wider.
- Use the right auxiliary gas: Auxiliary gases such as nitrogen or oxygen can not only help remove the molten material, but also cool the cutting area, reducing the heat effect and the kerf width.
- Adjust gas pressure: The right gas pressure helps to effectively remove the molten material and avoid burrs and residues on the cut edge.
- Choose the right nozzle diameter and type: The size and shape of the nozzle will affect the flow of the auxiliary gas and the cutting quality. Choosing the right nozzle can reduce the kerf width.
- Use high-quality optics: Keeping the optics of the laser system clean and calibrated to ensure the quality of the laser beam can reduce the divergence of the laser during the cutting process, thereby reducing the kerf width.
- Optimize the laser beam mode: Use single-mode or fundamental mode laser beams, which have better focusing characteristics and can achieve smaller cuts during the cutting process.
- Use advanced control software: Modern laser cutting machines are usually equipped with advanced control software that can adjust cutting parameters in real time to adapt to different cutting conditions.
- Perform material pretreatment: In some cases, pretreatment of the material, such as removing surface coatings or cleaning the surface, can increase the absorption rate of the laser and thus reduce the cut width.
- Perform multiple cuts: For very fine cutting requirements, the cut width of a single cut can be reduced by performing multiple cuts on the same track.
How little kerf can a laser cutter make
Laser cutting machines are capable of making very small cuts, the exact size of which depends on several factors:
Laser type: Different types of laser cutting machines (such as CO2, fiber, and YAG) have different cutting capabilities and precision.
Material properties: The type and thickness of the material being cut will affect the size of the cut. Generally, thinner materials will allow for smaller cuts.
Laser power and settings: The power and mode in which the laser machine operates will affect the accuracy of the cut. Lower power and finer settings will allow for smaller cuts.
Material surface: The smoother the material surface, the better the cut quality, which will help to achieve a smaller cut.
Cutting thickness: For materials less than 1mm thick, the cut can be very smooth and fine
FAQ
Does nozzle affect kerf when laser cutting
Yes, the nozzle can indirectly affect kerf width in laser cutting.
While the nozzle itself doesn’t physically determine the kerf (the width of the cut), it plays a crucial role in the cutting process that influences kerf size.
How can the size of a laser cutting kerf be controlled?
The size of the cutting kerf can be effectively controlled by adjusting parameters such as laser power, cutting speed, and focal length.
Is the laser cutting kerf the same for different materials?
No, the size of the laser cutting kerf varies for different materials due to their varying thermal properties, reflectivity, and other physical characteristics.
How can the dimensional errors caused by the laser cutting kerf be compensated for?
Dimensional errors caused by the cutting kerf can be compensated for by adjusting the drawings in CAD software or modifying the cutting path during programming.
