The development of industry: Industry 1.0, marked by steam engines, opened the door to mechanized production; Industry 2.0, with electrification as the core, realized large-scale production; and Industry 3.0, dominated by informatization, made automated production possible. Today, we are standing at the forefront of the era of Industry 4.0, a new industrial revolution that will completely reshape the face of the manufacturing industry.
The global manufacturing industry is currently facing a series of challenges such as production efficiency bottlenecks, uneven product quality, and cost control difficulties. The market demand for personalized products continues to rise, and higher requirements are placed on production flexibility and response speed.
The 4th industrial revolution provides unprecedented opportunities for the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry. It is not just a simple accumulation of new technologies, but also a new production paradigm that will profoundly change the operating model of enterprises, the ecological structure of industries, and the economic competitiveness of countries and regions.
This article will mainly explain to you “what is industry 4.0 meaning”, hoping to be helpful for industrial production and manufacturing.
What Is the Industrial Revolution
The industrial revolution refers to a series of major economic, social and technological changes in human history, usually divided into four main stages.
Industrial Revolution Development History
First Industrial Revolution (1760s-1840s)
- Origin: It began in Britain in the 1760s and marked the transition from manual labor to machine production.
- Main technologies: It was marked by the widespread use of steam engines, especially the steam engine improved by Watt, which promoted the development of industries such as textiles, mining and transportation. The invention of the spinning jenny is regarded as the beginning of this revolution.
- Social impact: It promoted the process of urbanization, formed the industrial bourgeoisie and the proletariat, and changed the traditional agricultural social structure. This period also triggered the workers’ movement, and workers fought against the bourgeoisie to improve their own conditions.
Second Industrial Revolution (late 19th century to early 20th century)
- Origin: This stage witnessed the development of electricity, internal combustion engines and chemical industries.
- Main technologies: The use of electricity greatly improved production efficiency and a series of new inventions emerged, such as electric motors, internal combustion engines and telephones.
- Social impact: It accelerated the process of globalization, promoted the development of transportation and communications, and made the market more closely connected. Some countries such as Germany, the United States and Japan emerged as world powers during this period.
The Third Industrial Revolution (1960s to 1990s)
- Origin: With the emergence of electronic technology and computers, information technology became the core of this period.
- Main technologies: The popularity of semiconductors, computers and the Internet has greatly changed the way information is disseminated and produced. Automation systems and network communications have been widely used.
- Social impact: It has shortened the distance between consumers and producers and changed business models and lifestyles.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (early 21st century to present)
- Origin: The ongoing revolution is characterized by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and blockchain.
- Main technologies: The integration of digital technology with physical technology and biotechnology has made production methods more intelligent and automated.
- Social impact: It has changed business models, economic structures, and life cultures, but also brought new challenges, such as data security and changes in employment structure.
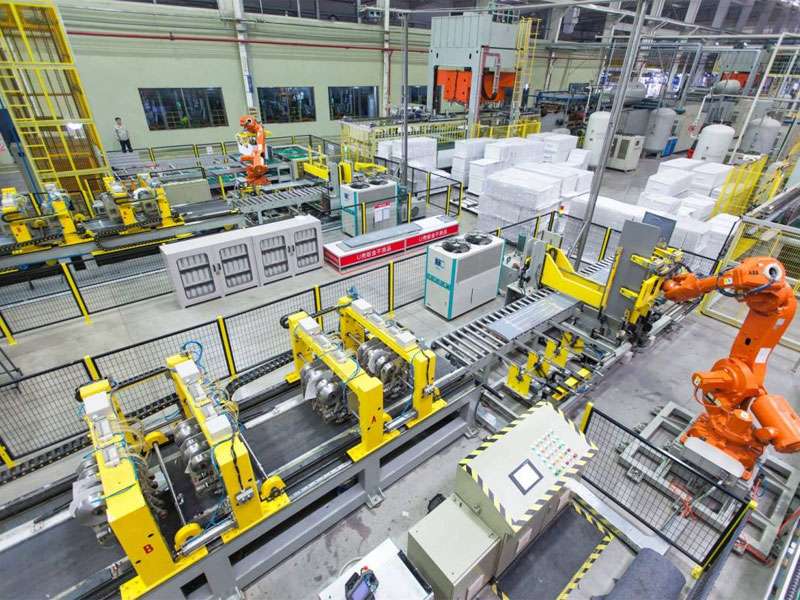

What Is Industry 4.0 / What is Industry 4.0 Meaning
Industry 4.0 definition (also known as the 4th industrial revolution, industrialization 4.0) uses cyber-physical systems (CPS) to digitize and intelligentize supply, manufacturing, and sales information in production, and finally achieve fast, effective, and personalized product supply. The physical entity and the digital virtual world are deeply integrated to form an intelligent and mutually collaborative network.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) describes it as a digital transformation covering the entire life cycle from product design to production, sales, and service, aiming to improve production efficiency and quality through intelligence.
When Did Industry 4.0 Start
The concept of the 4th industrial revolution was first proposed at the Hannover Industrial Fair in Germany in 2011, aiming to enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing industry through digitalization and intelligent technology. This strategy was promoted by the German government and included in the “High-Tech Strategy 2020 Action Plan” in 2013. Key figures include Henning Kagermann, president of the German National Academy of Science and Engineering and one of the main advocates of Industrie 4.0.
The fourth industrial revolution builds intelligent production systems by integrating emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and big data to achieve more efficient and flexible manufacturing processes. This strategy emphasizes not only technological innovation, but also the combination of traditional industries with digital technologies to adapt to rapidly changing market demands. Klaus Schwab, founder of the World Economic Forum, has also actively promoted this concept, emphasizing its importance to the global economy.

Core technologies of the 4th industrial revolution
Internet of Things (IoT): In Industry 4.0, IoT is the key to achieve device interconnection. By installing smart sensors in various links such as production equipment, sensors, and logistics systems, these devices can collect and transmit data in real time.
Big data and analysis: Massive amounts of data are constantly generated in the Industry 4.0 environment, and big data analysis technology is a powerful tool to mine the value of this data. Enterprises can optimize production processes by analyzing production data, such as predicting equipment failure time by analyzing machine operation data, arranging maintenance in advance, and reducing downtime. At the same time, by analyzing market data and customer feedback data, enterprises can better understand consumer needs and adjust product design and production plans.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Artificial intelligence is increasingly used in Industry 4.0. In terms of quality control, machine learning algorithms can automatically identify product defects by learning from a large number of product images or detection data. In production scheduling, artificial intelligence systems can dynamically schedule according to multiple factors such as order quantity, equipment status, and personnel arrangements to improve production efficiency.
Cloud computing: Cloud computing provides powerful data storage and computing power support for Industry 4.0. Enterprises no longer need to build huge data centers on their own, but can store data in the cloud and use computing resources in the cloud for data analysis and processing. This enables small and medium-sized enterprises to enjoy advanced information technology services at a lower cost, accelerating their digital transformation.
Industrial Automation and Robotics: Advanced automated production lines and intelligent robots are important signs of Industry 4.0. Industrial robots are no longer simple repetitive labor tools, they have higher intelligence and flexibility. Collaborative robots can work safely with human workers in the same space to complete complex assembly tasks. Automated production lines can be quickly adjusted according to different product requirements to achieve multi-variety, small-batch production.

Advantages of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Advantages for enterprises
Improve production efficiency: Industry 4.0 has achieved significant efficiency improvements by optimizing production processes. For example, the use of automated logistics systems can reduce material handling time, and intelligent scheduling systems can shorten production cycles. At the same time, the interconnection and real-time monitoring between equipment enable faults in the production process to be discovered and resolved in a timely manner, reducing downtime. Take a furniture manufacturing company as an example. After introducing Industry 4.0 technology, the production efficiency has increased by more than 30% through automated optimization of metal sheet cutting, processing, assembly and other links.
Enhance product quality: Using real-time monitoring and data analysis technology, companies can strictly control every link in the production process. In pharmaceutical production, the stability and consistency of pharmaceutical quality can be ensured by accurately monitoring and controlling parameters such as temperature, humidity, and pressure in the production environment, as well as real-time detection of raw material quality. The quality traceability system can quickly locate the source of quality problems and take timely measures to avoid the spread of problematic products.
Reduce costs: In terms of cost control, Industry 4.0 plays an important role. On the one hand, automation and intelligence reduce labor costs, and robots can undertake some dangerous, repetitive and high-intensity work. On the other hand, through precise production planning and material management, the waste of raw materials and inventory backlogs are reduced.
Improve innovation capabilities: Industry 4.0 provides fertile soil for corporate innovation. Enterprises can use digital technology to innovate in product design, such as rapid prototyping of complex structural products through 3D printing technology, accelerating product development cycles. At the same time, new business models are constantly emerging, such as the product as a service (PaaS) model, where companies no longer simply sell products, but provide product usage services, which brings new profit channels to companies.

Impact on industry and economy
Industrial chain upgrade: Industry 4.0 promotes closer collaboration between upstream and downstream companies in the industrial chain. In the aerospace industry, engine manufacturers, fuselage manufacturers, parts suppliers, etc. have achieved information sharing and collaborative design and production through the Industry 4.0 platform. This collaboration upgrades the efficiency and competitiveness of the entire industrial chain, shortening the product development cycle and improving quality. It also promotes the development of some emerging industries, such as industrial software, smart sensors and other related industries.
Create new employment opportunities and skill requirements: With the advancement of Industry 4.0, new jobs have emerged. Data analysts need to mine and analyze massive amounts of production and market data to support corporate decision-making; robotics engineers are responsible for designing, maintaining and programming intelligent robots; industrial Internet security experts are responsible for ensuring the security of corporate networks and data. Traditional workers also need to transform their skills and master digital operation and maintenance skills.
Enhance the industrial competitiveness of countries or regions: In the global economic competition, countries and regions that implement Industry 4.0 have shown strong advantages. As one of the initiators of Industry 4.0, Germany has maintained its leading position in the international market through digital transformation in its automobile manufacturing, mechanical equipment and other industries. Enterprises in these countries and regions can respond to market demand with higher quality, lower cost and faster speed, win more market share, and enhance the economic strength of the entire country or region.
Application Scenarios of the 4th Industrial Revolution
Smart Manufacturing
Smart Manufacturing is an important part of Industrial Revolution 4th, which improves production efficiency through automation and data-driven methods. For example, using real-time data to monitor equipment status can detect and solve problems in a timely manner.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses sensors to monitor equipment status and detect potential failures in advance. This approach not only reduces downtime but also reduces maintenance costs.
Supply Chain Optimization
Industrial Revolution 4th makes it possible to share and coordinate information in all links of the supply chain. Through real-time data analysis, companies can quickly respond to market changes and improve supply chain efficiency.
Personalized Customization
With the increasing diversification of consumer needs, personalized customization has become a trend. Industry 4.0 enables companies to quickly adjust production plans according to customer needs and achieve small batch diversified production.

Advantages and challenges of industrial revolution 4
Advantages
- Improve production efficiency: Through automation and intelligent means, production efficiency can be greatly improved.
- Reduce costs: Optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and thus reduce operating costs.
- Improve product quality: Real-time monitoring and data analysis help companies improve product quality.
- Enhance market competitiveness: Quickly respond to market changes and improve customer satisfaction.
Challenges
- Technology implementation is complex: Integrating new technologies requires expertise and experience.
- Talent shortage: The demand for highly skilled talents is increasing, but the supply in the market is insufficient.
- Data security and privacy issues: As the amount of data increases, protecting sensitive information becomes more important.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is a milestone in industrial development. It changes the face of manufacturing, connects the physical and digital worlds, opens a new era of intelligent production, promotes industrial upgrading and economic structure optimization, and is the key to corporate competition and regional development. In the future, it will integrate innovation and expand its application areas. Enterprises should actively embrace it to help development and progress.
