Laser cutting is a powerful technology used to cut various materials with incredible precision. But if you’ve ever looked into laser cutting, you may have encountered two main types: 2d laser cutting machine
and 3d laser cutting machine. Although they sound similar, they are used for different applications and have distinct advantages.
In this article, we’ll explore the difference between 2d and 3d laser cutting and help you decide which method might be right for your needs.
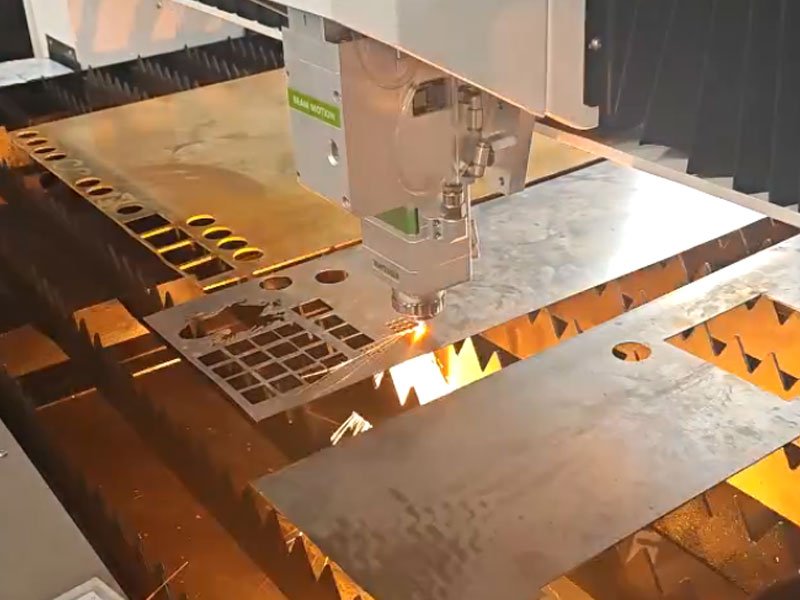
What is 2D Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
2D laser cutting involves cutting materials that are flat. This process is widely used for creating parts from metal sheets, plastics, wood, or fabric. The laser beam moves in two dimensions (hence “2D”) to follow a specified path and cut through the material.
2D laser cutting equipment is fast, accurate and repeatable. It can also be used to cut a variety of materials, making it a versatile choice for many applications.
Advantages of 2D Laser Cutting Machine Equipment
- Affordable Production: Ideal for bulk manufacturing, keeping costs low while maintaining high quality.
- Quick Processing: Fast cutting speeds make it suitable for quick turnaround times.
- Easy to Learn: Simpler to operate, even for beginners.
- Versatile Material Use: Compatible with a wide array of materials, including metals and textiles.
How Does 2D Laser Cutting Work?
- Design Creation:
- A design is prepared using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which instructs the machine where to cut.
- Setup:
- The flat material is laid on the cutting bed. The laser head, controlled by CNC (Computer Numerical Control), is positioned above the material.
- Cutting:
- The laser beam precisely cuts the material by moving along the design paths, achieving clean and accurate cuts.
- Finishing Touches:
- After cutting, any leftover pieces or edges might need cleaning or additional processing.
Features of 2D Flate Laser Cutting
- Precision: It offers highly accurate cuts, making it ideal for components that need to fit together precisely.
- Speed: It’s fast, especially for straightforward designs and thinner materials.
- Versatility: Suitable for a broad range of materials like metals, textiles, and plastics.
- Cost-effective: Typically less expensive than 3D cutting, particularly for large scale productions.
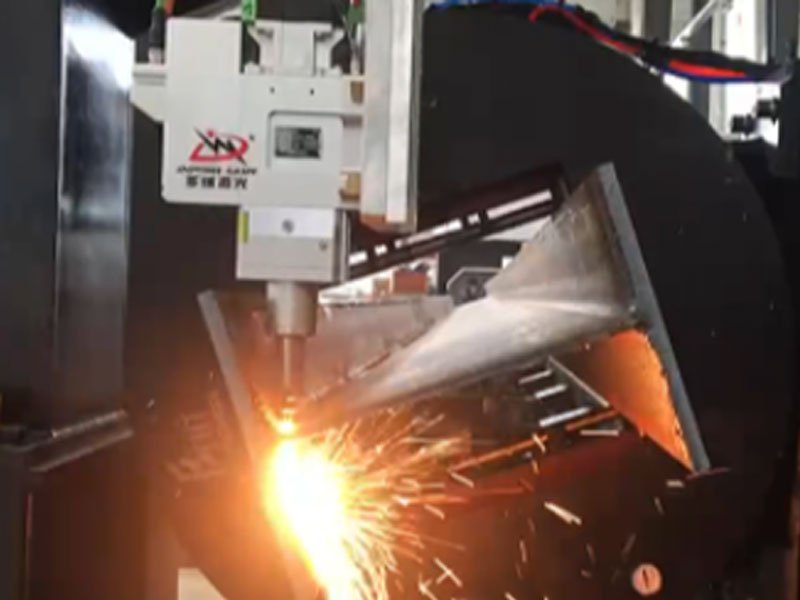

What is 3D Laser Cutting?
3D laser cutting is a more advanced process used to cut materials with depth and complexity. Unlike 2D cutting, it can handle objects with multiple dimensions and angles, such as pipes, tubes, and intricate three-dimensional parts.
3D fiber laser cutting machine has greater design flexibility and manufacturability advantages. It can be used to create complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
Advantages of 3D Laser Cutting Machine Equipment
- Handles Complexity: Suitable for intricate designs with varying shapes and angles.
- Versatile Angling: Capable of cutting at different angles for more elaborate parts.
- Precision on Curves: Maintains accuracy on curved and irregular surfaces.
- Reduces Machining Steps: Often negates the need for additional machining, saving time and labor.
How Does Laser Cutting Machine 3D Work?
- Design Creation:
- A 3D model is developed in CAD software, accounting for the object’s full geometry.
- Setup:
- The material can be any shape, such as a cylinder or cube. The laser head or the workpiece itself is manipulated to access different angles.
- Cutting:
- The laser follows the 3D design path, cutting with precision. The machine adjusts the laser’s angle and depth as needed to achieve detailed cuts.
- Post-Processing:
- The finished product may require additional polishing or refining to ensure smoothness.
Features of 3D Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
- Complexity Handling: Excellent for intricate designs on varied surfaces.
- Flexibility: Capable of cutting at multiple angles and depths.
- High Precision: Accurate cuts even on curved surfaces.
- Time-efficient: Eliminates the need for further machining processes, saving time.

Application areas for 2D and 3D laser cutting
Applications of 2D laser cutting
2D laser cutting is mainly used for cutting flat materials, and is suitable for various thin plates and medium-thick materials. The following are some of the main application areas of 2D laser cutting:
Metal processing
- Automobile manufacturing: 2D laser cutting is widely used in the manufacture of automotive parts, such as chassis components, brackets and panels. Its high precision and fast cutting ability make it an important tool in automobile manufacturing
- Machinery manufacturing: Used to cut various mechanical parts and components, ensuring high precision and consistency.
Advertisement production
- Signage production: 2D laser cutting can produce complex signs and billboards with high precision and beautiful cutting effects.
- Decorations: Used to make a variety of metal and plastic decorations to meet personalized customization needs.
Electronic circuit boards
Circuit board processing: 2D laser cutting is used to cut and engrave circuit boards, ensuring high precision and clean cutting edges.
Textile industry
Fabric cutting: 2D laser cutting is used to accurately cut fabrics, suitable for custom-designed clothing and textiles.
Woodworking and furniture manufacturing
Wood board cutting: Used to cut various wood board materials to make furniture and wood products.
Application Areas of 3D Laser Cutting
3D laser cutting can handle complex three-dimensional shapes and geometries, making it suitable for materials of various thicknesses. Here are some of the main application areas of 3D laser cutting:
Aerospace
- Complex Part Manufacturing: 3D laser cutting is used to manufacture complex parts in the aerospace industry, such as fuel lines and structural components. Its high precision and flexibility make it a key technology in aerospace manufacturing.
Medical Devices
- Medical Implants: It is used to create precise medical implants and devices, ensuring high accuracy and biocompatibility.
Automotive Manufacturing
- Body and Components: 3D laser cutting is utilized in automotive manufacturing to cut and shape car bodies and various components, such as exhaust pipes and support structures. Its efficient and precise cutting capabilities improve production efficiency and product quality.
Art and Sculpture
- Artwork Creation: 3D laser cutting is used to create complex artworks and sculptures, allowing for highly detailed and intricate designs.
- Decorative Items: It is also used to produce various metal and plastic decorative items, meeting the demand for personalized customization.
Construction Industry
- Structural Component Manufacturing: It is used to cut and manufacture structural components in the construction industry, such as steel beams and support structures. Its high precision and flexibility make it an important tool in the construction industry.
Furniture Manufacturing
- Metal Furniture: 3D laser cutting is used to manufacture various components of metal furniture, ensuring high precision and consistency.
Energy Industry
- Pipes and Equipment: It is used to manufacture pipes and equipment in the oil, natural gas, and other energy industries, ensuring efficient and precise cutting.
Mold Making
- Mold Processing: 3D laser cutting is used for trimming and drilling molds, reducing costs, shortening manufacturing cycles, and improving the quality of parts.
2D vs 3D Laser Cutting : Choose Which One
| Aspect | 2D Laser Cutting | 3D Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions and Applications | Dimensions: Works exclusively with flat surfaces. Applications: Suitable for creating flat components like panels, signs, gears, and enclosures. | Dimensions: Capable of cutting three-dimensional objects. Applications: Ideal for complex shapes, such as automotive parts, sculptures, and aerospace components. |
| Equipment and Setup | Equipment: Simpler machinery that’s generally less expensive. Includes a laser source, mirrors, a lens, and a cutting table. Setup: Easier and quicker, especially for straightforward tasks. | Equipment: Advanced machinery that can move the laser head in multiple axes or rotate the material. Setup: Requires more expertise and time to configure, particularly for intricate designs. |
| Precision and Accuracy | Precision: Offers excellent accuracy on flat surfaces, making it suitable for precise fitting parts. Accuracy: Reliable for simple and moderately complex designs. | Precision: Maintains high precision on complex geometries. Accuracy: Provides accurate cuts at varying angles and depths. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Speed: Faster for simple cuts and designs, especially in mass production. Efficiency: Highly efficient for flat sheets, resulting in minimal material waste. | Speed: Generally slower due to the complexity of handling multiple angles. Efficiency: Efficient for producing intricate parts that would require multiple steps in traditional machining. |
| Cost Considerations | Initial Cost: Lower setup and machinery costs. Operational Cost: Economical for large-scale production of simple parts. | Initial Cost: Higher cost due to sophisticated machinery. Operational Cost: More expensive, but offers savings by eliminating additional machining processes. |
Conclusion
2D fibre laser cutting machine is like drawing on paper – flat and fast. 3D laser cutting is like sculpting – complex and versatile. Both are awesome in their own ways.Remember, the best choice depends on what you’re making, your budget, and the materials you’re using. Whether you go 2D or 3D, laser cutting is an awesome technology that’s changing the way we make things!
