Cutting sheet metal is a fundamental skill in various industries, from automotive to construction and manufacturing. Whether you’re a professional or a DIY enthusiast, knowing the right techniques and tools to use is crucial for achieving clean, precise cuts.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different methods of cutting sheet metal, the tools required, and tips to ensure safety and accuracy.
Types of sheet metal
Sheet metal cutting involves slicing through metal sheets to create parts, components, or finished products. The choice of cutting method depends on the type of metal, its thickness, and the desired level of precision. Common types of sheet metal include:
- Steel (Carbon and Stainless)
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass
Different material cutting methods
How to Cut Steel Sheet Metal
To cut steel sheet metal, you can use tools like tin snips for thin sheets, an angle grinder for thicker sheets, or a laser cutter for precise cuts. Ensure the steel is clamped securely and follow safety protocols such as wearing gloves and safety glasses.
How to Cut Aluminium Sheet Metal
Aluminium sheet metal can be cut with a jigsaw using a metal-cutting blade, electric shears for faster cuts, or a laser cutter for high precision. Use a lubricant to reduce friction and prevent the blade from gumming up.
How to Cut Galvanized Sheet Metal
Cut galvanized sheet metal using tin snips for manual cuts, an angle grinder for thicker sheets, or electric shears for efficiency. Wear a mask to avoid inhaling zinc fumes and clean the cut edges to prevent corrosion.
How to Cut Brass Sheet Metal
Brass sheet metal can be cut with a jigsaw fitted with a metal-cutting blade, a hacksaw for detailed work, or a laser cutter for intricate shapes. Brass is softer than steel, so ensure the blade is suitable for non-ferrous metals.
How to Cut Stainless Steel Sheet Metal
Cut stainless steel sheet metal with an angle grinder for thicker sheets, electric shears for medium thickness, or a plasma cutter for precision. Stainless steel is tough, so use tools with high power and appropriate blades.
How to Cut Copper Sheet Metal
Copper sheet metal can be cut using tin snips for thin sheets, a jigsaw for curves and detailed cuts, or a laser cutter for precision. Copper is malleable, so handle it carefully to avoid warping.
How to Cut Thin Sheet Metal
Thin sheet metal can be cut using tin snips for straight cuts, a nibbler for intricate shapes, or electric shears for efficiency. Ensure the sheet is clamped to prevent bending and wear protective gloves to handle sharp edges.

How to Cut A Hole in Sheet Metal
How to Cut Perfect Holes in Sheet Metal
To cut perfect holes in sheet metal, use a hole saw for larger holes or a step drill bit for smaller, precise holes. Ensure the sheet is securely clamped and use a center punch to mark the hole’s center for accuracy.
How to Cut a Large Hole in Sheet Metal
For a large hole, use a hole saw attached to a power drill. Clamp the sheet metal securely, mark the center with a punch, and drill slowly to maintain control and precision.
How to Cut a Circular Hole in Sheet Metal
Use a hole saw or a circle cutter to cut a circular hole. Secure the metal sheet, mark the center, and drill slowly. For larger circles, a jigsaw with a metal-cutting blade can also be used.
How to Cut a Round Hole in Sheet Metal
To cut a round hole, use a step drill bit or hole saw. Mark the hole center, clamp the sheet, and drill at a steady speed to avoid deforming the metal.
How to Cut a Rectangular Hole in Sheet Metal
For a rectangular hole, mark the outline, drill pilot holes at the corners, and use a jigsaw with a metal-cutting blade to cut along the lines. File the edges for a clean finish.

How to Cut a Square Hole in Sheet Metal
Mark the square outline, drill pilot holes at the corners, and use a jigsaw or nibbler to cut along the lines. Use a file to clean up the edges.
How to Cut a Small Square Hole in Sheet Metal
Use a punch tool for small square holes or drill small pilot holes at the corners and cut with a jigsaw or a file. Ensure precise measurements for accuracy.
How to Cut a Hole in 16 Gauge Sheet Metal
For 16 gauge sheet metal, use a step drill bit for small holes or a hole saw for larger holes. Secure the sheet, mark the hole, and drill slowly to maintain precision.
How to Cut a 1 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
Use a 1-inch hole saw or a step drill bit. Mark the center, secure the sheet, and drill at a controlled speed to achieve a clean cut.
How to Cut a 2 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
To cut a 2-inch hole, use a 2-inch hole saw. Mark the center, clamp the sheet, and drill steadily. A hole punch can also be used for cleaner edges.
How to Cut a 3/4 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
Use a 3/4 inch step drill bit or hole saw. Secure the sheet, mark the center, and drill slowly to ensure a clean cut.
How to Cut a 4 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
For a 4-inch hole, use a 4-inch hole saw. Mark the center, clamp the sheet, and drill at a steady speed to maintain accuracy and clean edges.
How to Cut a 6 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
Use a 6-inch hole saw or a jigsaw for a 6-inch hole. Secure the sheet, mark the center, and drill carefully. For jigsaw, cut along the marked circle after drilling a starter hole.
How to Cut a 7 Inch Hole in Sheet Metal
To cut a 7-inch hole, use a jigsaw with a metal-cutting blade. Mark the circle, drill a starter hole, and cut along the marked line with steady hands. Secure the sheet to prevent movement.

How to cut sheet metal ductwork
Cutting sheet metal for ductwork requires precision and the right tools to ensure proper fit and functionality. Whether you’re installing HVAC ducts or fabricating custom ductwork for a project, here’s a step-by-step guide to cutting sheet metal effectively:
Materials and Tools Needed:
- Sheet Metal: Choose the appropriate gauge and type of sheet metal for your ductwork (commonly galvanized steel or aluminum).
- Measuring Tape or Ruler: For accurate measurements.
- Marker or Scribe: To mark cutting lines on the sheet metal.
- Straight Edge: For guiding cutting tools.
- Cutting Tools: Depending on the thickness and type of metal, options include:
- Tin snips or aviation snips for thinner gauges.
- Electric shears for medium thickness.
- Circular saw with a metal-cutting blade, jigsaw, or nibbler for more precise cuts.
- Plasma cutter or laser cutter for thicker metals and complex shapes.
- Safety Gear: Gloves, safety glasses, and hearing protection, especially when using power tools.
Tips for Cutting Sheet Metal Ductwork:
- Plan Ahead: Measure and plan your cuts carefully to minimize waste and ensure accurate fabrication.
- Use Proper Tools: Choose cutting tools appropriate for the thickness and type of sheet metal you are working with to achieve clean cuts and precise shapes.
- Safety First: Always wear appropriate safety gear when cutting and handling sheet metal to protect against sharp edges, sparks, and metal debris.when cutti
- Test Fit: Before final assembly and installation, test fit all components to verify measurements and ensure a proper fit.
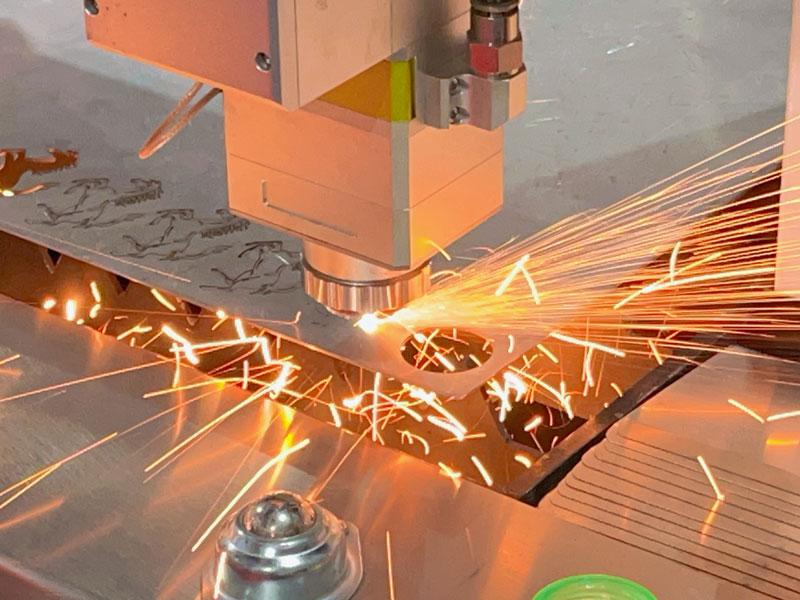

How to cut a cone shape out of sheet metal
Cutting a cone shape out of sheet metal requires careful planning and precise execution to achieve a smooth and accurate result. Follow these steps to create a cone shape from sheet metal:
Materials and Tools Needed:
- Sheet Metal: Choose a suitable gauge and type of sheet metal for your project.
- Marker or Scribe: For marking the cutting lines.
- Measuring Tape or Ruler: To measure and mark dimensions accurately.
- Cutting Tools: Depending on the thickness of the sheet metal, you may need:
- Tin snips or aviation snips for thinner metal.
- Electric shears or a jigsaw with a metal-cutting blade for medium thickness.
- Plasma cutter or laser cutter for thicker metal.
Tips for Cutting a Cone Shape:
- Precision is Key: Measure and mark accurately to ensure the cone shape fits together properly.
- Choose the Right Tools: Use cutting tools appropriate for the thickness and type of sheet metal you are working with.
- Practice Safety: Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses, especially when using power tools.
- Consider Material Properties: Different metals may require different cutting techniques and tools. Adjust your approach accordingly.

Best tool to cut sheet metal
Hand Tools
1. Tin Snips/Sheet Metal Shears
- Description: Tin snips are hand tools similar to scissors, designed for cutting thin sheet metal.
- Best For: Cutting thin sheets (up to 18 gauge for steel, 16 gauge for aluminum).
- Usage Tips: Use straight-cut snips for straight lines and left- or right-cut snips for curves. Ensure the blades are sharp for clean cuts.
2. Hacksaw
- Description: A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw suitable for cutting metal.
- Best For: Small, precise cuts in thin metal sheets.
- Usage Tips: Use a high-quality blade and apply steady pressure. Clamp the metal securely to avoid movement.
3. Nibbler
- Description: Nibblers are hand-operated tools that punch out small bits of metal.
- Best For: Cutting intricate shapes and curves.
- Usage Tips: Follow the cutting line carefully to avoid distorting the metal.
Power Tools
1. Electric Shears
- Description: Electric shears cut through metal sheets with a motorized blade.
- Best For: Faster, more efficient cutting of thin to medium-thickness sheets.
- Usage Tips: Ensure a steady hand and follow safety instructions. Keep the blades sharp and clean.
2. Angle Grinder
- Description: An angle grinder is a versatile tool with a rotating abrasive disc.
- Best For: Cutting thicker metal sheets and rough cuts.
- Usage Tips: Use the appropriate cutting disc for metal and wear safety gear to protect from sparks and debris.
3. Jigsaw
- Description: A jigsaw is a power tool with a reciprocating blade.
- Best For: Cutting curves and complex shapes in thin to medium-thickness sheets.
- Usage Tips: Use a metal-cutting blade and adjust the speed setting according to the material thickness.
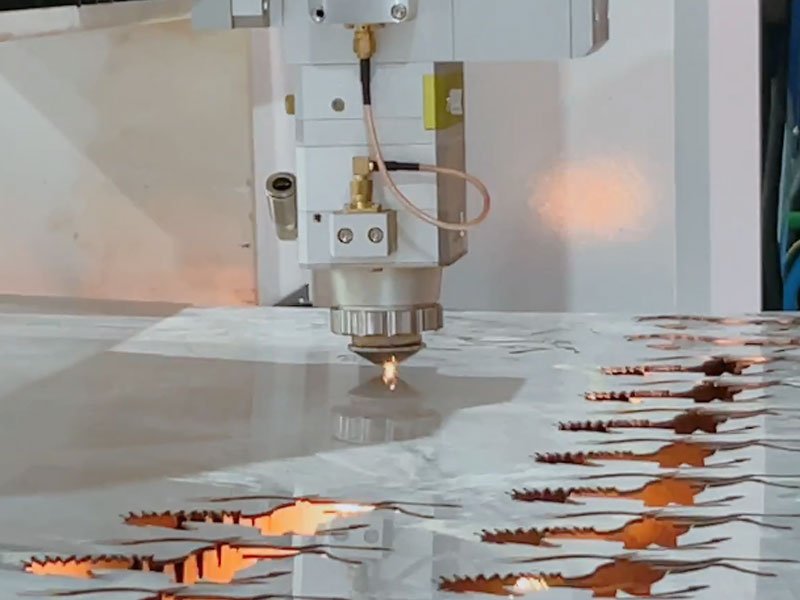

Easiest way to cut sheet metal
1. Laser Cutting
- Description: Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to cut metal sheets with high precision.
- Best For: High-precision cuts, complex shapes, and thick materials.
- Usage Tips: Requires specialized equipment and safety precautions. Ideal for industrial applications.
2. Plasma Cutting
- Description: Plasma cutting uses a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through metal.
- Best For: Cutting thick sheets and conductive metals.
- Usage Tips: Ensure proper grounding and follow safety guidelines to avoid electrical hazards.
3. Water Jet Cutting
- Description: Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive particles to cut metal.
- Best For: Cutting without generating heat, suitable for thick and sensitive materials.
- Usage Tips: Requires precise control and setup. Ideal for materials that may be affected by heat.
How to Cut Sheet Metal Safely
Safety is paramount when working with sheet metal due to the sharp edges and potential hazards associated with cutting tools. Follow these safety tips:
- Wear Protective Gear: Use gloves, safety glasses, and long sleeves to protect from sharp edges and flying debris.
- Secure the Metal: Clamp the metal sheet securely to prevent movement during cutting.
- Use the Right Tool: Choose the appropriate tool for the material and thickness to avoid accidents.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere to the tool manufacturer’s safety guidelines and maintenance recommendations.
- Keep the Work Area Clean: Remove any clutter and ensure adequate lighting to avoid mishaps.
Tips for Achieving Clean Cuts
- Mark Your Cuts Clearly: Use a fine-tip marker or scribe to mark your cutting lines precisely.
- Practice Steady Hand Movements: Maintain a steady hand and consistent pressure to ensure smooth cuts.
- Keep Blades Sharp: Regularly sharpen or replace blades to maintain cutting efficiency and precision.
- Deburr Edges: Use a file or deburring tool to smooth out any rough edges after cutting.
